Shocking Data Points
Explore how vegetarianism is declining across major U.S. cities, backed by recent data and expert insights.
1. Portland Leads in Plant-Based Dining
Portland residents order vegan and vegetarian food 148% more frequently than the U.S. average, making it the most vegetarian-friendly city in the country. Source
2. Decline in Veganism Nationwide
Interest in veganism has waned since its peak in early 2020, with Google searches for “vegan” dropping significantly and sales of plant-based meat brands like Beyond Meat and Impossible Foods declining. Source
3. Increase in Meat Consumption
Despite a slight rise in households avoiding meat, overall meat consumption in the U.S. has increased by 15%, reaching some of the highest global rates. Source
4. Plant-Based Milk Outpaces Cow Milk
Consumption of plant-based milk has grown by 61% compared to cow milk, with soy milk leading as the most popular plant-based milk. Source

5. Surge in Vegan Food Launches
Yearly growth for vegan and plant-based food and beverage launches increased from 21% in 2015 to 58% in 2019, indicating a growing interest in plant-based diets. Source
6. Vegan Baby Food Market Growth
The vegan baby food market has increased by 10% from 2016 to 2021, reflecting a shift towards plant-based options for infants. Source
7. Rise in Plant-Based Meat Sales
Vegan meat sales grew by 74% from 2018 to 2021, showcasing a significant shift towards plant-based protein sources. Source
8. Plant-Based Milk Market Share
Plant-based milk now makes up 16% of all milk sold in sales alone, and 35% of the entire plant-based food market. Source
9. Increase in Vegan Product Availability
By 2021, plant-based online retail showed a 199% year-on-year increase, making it the ‘category of the year’ according to 101data. Source
10. Growth in Vegan Restaurant Listings
Central LA currently has 61 fully vegan restaurants, 145 vegan businesses of various types, and 652 vegan-friendly listings, indicating a thriving vegan scene. Source
11. Decline in Veganism Among Influencers
High-profile advocates have faltered, and formerly vegan-friendly establishments have reintroduced animal products, contributing to the decline in veganism. Source
12. Shift Towards High-Protein Diets
The rising popularity of high-protein diets has further marginalized veganism, as meat continues to dominate perceptions of protein sources. Source
13. Vegan Alternatives Falling Short
Vegan alternatives often failed to meet taste expectations, particularly in blind taste tests, leading to a decline in their popularity. Source
14. Lack of Government Support
Governments offered little support for veganism compared to subsidies for electric cars, hindering its growth and adoption. Source
15. Decline in Idealism
A decline in idealism, especially amid global crises, has reduced motivation to make lifestyle sacrifices for ethical reasons, impacting veganism’s popularity. Source
16. Increase in Meatless Households
While a small segment opts out of meat, the majority’s meat purchases have risen by 15%, highlighting a complex dietary trend. Source
17. Growth in Plant-Based Food Sales
Plant-based food sales have grown three times faster than those for non-plant-based foods, indicating a shift in consumer preferences. Source
18. Rise in Vegan Milk Consumption
Global consumption of plant-based milk grew from half a kilo in 2013 to a full kilogram in 2020, reflecting increased demand. Source
19. Increase in Vegan Egg Alternative Market
The vegan egg alternative market experienced a boom, with a growth of 700% since 2018, showcasing innovation in plant-based products. Source
20. Growth in Vegan Milk Market Cap
The plant-based milk market cap was worth $8 billion in 2016 and is expected to grow to $21 billion by 2024, indicating a significant market expansion. Source
For more information on plant-based diets and their impact, visit EatingWell.
Urban Challenges to Vegetarian Lifestyles
Many U.S. cities face challenges in supporting vegetarian lifestyles due to limited access to fresh produce in certain neighborhoods. Urban food deserts and higher costs of organic produce make it difficult for residents to maintain consistent plant-based diets, contributing to the decline observed in multiple metropolitan areas.
Socioeconomic Factors Affecting Plant-Based Choices
Income and education levels strongly influence dietary habits. Research indicates that lower-income households are less likely to follow vegetarian diets due to affordability and convenience of processed foods, while higher-income groups are more likely to experiment with plant-based alternatives. These socioeconomic disparities explain part of the declining vegetarian trends across U.S. cities.
Cultural Preferences and Meat-Centric Traditions
Cultural traditions in many cities favor meat-heavy diets, making vegetarianism less common. Festivals, social gatherings, and regional cuisine often emphasize meat as the central ingredient, which can discourage long-term adherence to plant-based eating.
Impact of Fast Food Availability
The proliferation of fast food chains in urban centers has made meat-heavy meals more accessible and affordable than vegetarian alternatives. This convenience factor contributes to declining vegetarian adherence, particularly among busy professionals and students.
Lack of Vegetarian Education in Schools
Many school programs across U.S. cities do not incorporate comprehensive education on vegetarian nutrition. Without proper guidance, children grow up unaware of the benefits and preparation techniques for plant-based diets, leading to lower adoption rates in adulthood.
Influence of Social Media and Pop Culture
Social media trends often promote high-protein, meat-based diets, particularly among fitness enthusiasts and influencers. These messages can overshadow vegetarian lifestyle benefits and contribute to the perception that meat consumption is superior for energy and muscle building.
Environmental Awareness Not Translating to Action
Despite increased awareness of environmental issues, many city residents fail to translate knowledge into dietary change. Urban populations may understand that plant-based diets reduce carbon footprints but still prioritize taste, convenience, and affordability, weakening vegetarian adherence.
Health Misinformation and Conflicting Advice
Conflicting health messages from experts and media outlets create confusion about plant-based diets. Some reports exaggerate deficiencies, while others oversimplify benefits, leaving urban residents unsure how to balance nutrition properly. This uncertainty contributes to dietary lapses and declining vegetarian trends.
Limited Availability of Specialty Vegetarian Products
In smaller or less diverse U.S. cities, specialty vegetarian foods like vegan cheese, plant-based meats, and fortified dairy alternatives are often scarce. Limited product availability reduces convenience and discourages sustained vegetarian eating patterns.
Workplace Eating Habits
Employees in urban corporate environments often have limited vegetarian options in cafeterias and restaurants. High-pressure work schedules lead to reliance on quick, meat-based meals, further decreasing the likelihood of maintaining vegetarian diets during weekdays.
Shift in Grocery Store Offerings
Although plant-based products have grown in popularity, major grocery chains still dedicate more shelf space to meat and dairy items. This imbalance influences purchasing behavior and reinforces meat consumption over vegetarian options in many urban neighborhoods.
Impact of Advertising and Marketing
Marketing campaigns for meat, dairy, and protein supplements heavily dominate media channels, overshadowing plant-based alternatives. Aggressive advertising increases the perceived desirability of meat, contributing to the decline of vegetarian diets among urban populations.
Religious and Festival Dietary Customs
Some religious practices involve meat consumption or festive meals centered on animal products. Residents participating in these traditions may intermittently abandon vegetarianism, which cumulatively lowers the overall adherence rates in cities with diverse religious communities.
Urban Lifestyle Stressors
High stress levels in urban environments affect eating habits. Many residents choose comfort foods high in fat and protein over healthier plant-based options. Stress-induced eating behaviors can erode commitment to vegetarian diets over time.
Generational Dietary Shifts
Older generations may be less inclined to adopt vegetarian diets due to established eating habits, while younger urban populations are more experimental. However, convenience-driven dietary patterns, social pressures, and fast food accessibility cause some younger adults to abandon vegetarianism despite initial interest.
Economic Pressures and Diet Choices
Urban residents often face economic pressures that influence their food choices. Plant-based diets, particularly organic or specialty vegetarian items, can be more expensive than meat-based meals. Many households prioritize affordability over nutritional philosophy, leading to a gradual decline in vegetarian adherence despite awareness of health benefits.
Time Constraints and Convenience Foods
Busy urban lifestyles leave little time for meal planning and preparation. Las Vegas, New York, and other major U.S. cities report that residents increasingly rely on fast food, pre-packaged meals, and restaurant dining. These convenient options often favor meat-heavy dishes, which undermines long-term vegetarian commitment.
Influence of Family Habits
Family dietary traditions significantly impact vegetarian adoption. Children raised in omnivorous households are less likely to maintain plant-based diets as adults. In urban areas where multi-generational families live together, meat-centric meals dominate home cooking, making vegetarianism harder to sustain.
Urban Food Marketing Trends
Restaurants, grocery stores, and media campaigns heavily promote meat products. In cities like Chicago and Atlanta, the marketing of protein-rich meat alternatives often overshadows vegetarian options, contributing to declining adoption rates. Aggressive advertising reinforces the perception that meat is essential for energy and growth.
Vegetarian Diet Misconceptions
Many residents hold misconceptions about vegetarian nutrition, such as believing protein or iron requirements cannot be met without meat. U.S. health surveys reveal that these beliefs discourage continued vegetarianism, even among educated populations who otherwise have access to plant-based options.
Limited Institutional Support
Schools, hospitals, and workplace cafeterias often offer limited vegetarian options, making it challenging to maintain a plant-based lifestyle outside the home. Urban institutions in cities like Los Angeles and New York have slowly begun expanding offerings, but adoption remains inconsistent.
Peer Pressure and Social Dining
Social influences in metropolitan areas affect dietary choices. Dining with friends, attending events, and participating in business lunches often revolves around meat-based meals. Peer pressure and social norms can erode vegetarian adherence, especially among younger adults.
Seasonal and Regional Food Preferences
Seasonal produce availability varies across U.S. cities, impacting vegetarian menu diversity. In colder climates like Minneapolis or Denver, limited access to fresh fruits and vegetables during winter months leads many to revert to meat-heavy diets for variety and satiety.
Health and Fitness Fads
The rise of high-protein and keto diet trends has shifted attention away from plant-based diets. Urban gyms, fitness influencers, and dietary coaches often promote animal protein as essential for muscle building, reducing interest in vegetarian nutrition among health-conscious populations.
Urban Transportation and Grocery Access
Limited access to full-service grocery stores in certain neighborhoods forces residents to shop at convenience stores or fast food outlets. Lack of access to fresh produce, especially in food deserts, discourages plant-based eating and contributes to declining vegetarian rates in urban communities.
Food Delivery and On-Demand Meals
The popularity of food delivery apps has increased access to meat-heavy restaurant meals. Urban residents often prioritize speed and convenience over nutrition, leading to reduced plant-based meal consumption. Vegetarian options are available but often less advertised or more expensive.
Psychological Comfort of Meat
Meat is often associated with comfort and emotional satisfaction. Urban stressors, long working hours, and lifestyle pressures make residents more likely to choose meat-based meals for psychological satisfaction, reducing the likelihood of sustained vegetarian diets.
Globalization and Cultural Food Imports
The influence of global cuisine introduces a variety of meat-centric dishes to U.S. cities. Restaurants offering international specialties may unintentionally marginalize vegetarian options, as diners are drawn to authentic meat-based recipes over plant-based alternatives.
Nutrition Label Confusion
Urban consumers often struggle to interpret nutrition labels for plant-based products. Misleading claims about protein content, calories, or additives can discourage the purchase of vegetarian foods. Confusion in the grocery aisle contributes to the decline in plant-based meal adoption.
Workplace Stress and Eating Patterns
High-stress urban work environments encourage quick, convenient meals that are often meat-heavy. Employees with long hours may forgo vegetarian options due to perceived inconvenience or lack of appealing alternatives, affecting long-term dietary habits.
Generational Shifts and Trend Adoption
While younger urban generations are more open to plant-based diets, lifestyle changes, travel, and social influences often lead them back to meat consumption. Older generations remain less likely to experiment with vegetarianism, creating a mixed generational adoption pattern across cities.
Impact of Urban Nightlife on Diet
Late-night urban dining often favors fast food and meat-heavy meals, especially in cities with active nightlife like New York, Las Vegas, and Miami. Bars, clubs, and late-night eateries offer limited vegetarian options, encouraging residents to consume meat-rich comfort foods instead of plant-based alternatives.
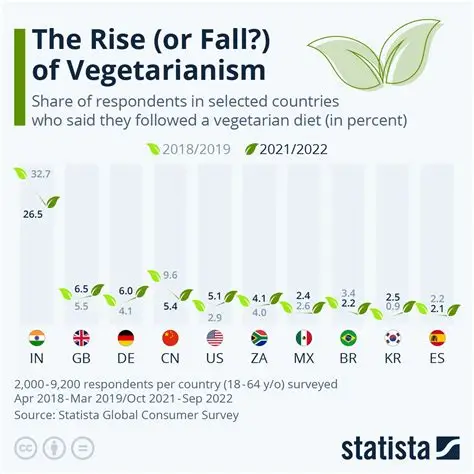
Influence of Celebrity Endorsements
Celebrity endorsements heavily influence dietary trends. Meat-centric fitness influencers and chefs often dominate social media, overshadowing vegetarian lifestyle advocates. This visibility contributes to the perception that meat-based diets are more desirable or effective, reducing vegetarian adoption.
Food Festivals and Culinary Trends
Food festivals in major cities frequently spotlight meat-centric dishes, grilling competitions, and BBQ events. While some festivals include vegetarian options, the emphasis on animal protein often drives consumer preference toward non-plant-based foods, affecting long-term dietary habits.
Impact of Restaurant Pricing
Vegetarian dishes in urban restaurants are often priced higher than meat-based meals, especially when using organic or specialty ingredients. Price disparities can discourage regular consumption of plant-based meals, contributing to declining vegetarian adherence across U.S. cities.
Fast Food Culture in College Campuses
College students frequently rely on campus dining halls and fast food due to convenience and budget constraints. While vegetarian options exist, meat-heavy meals dominate both choice and availability, influencing student eating patterns and reducing long-term vegetarian commitment.
Effect of Urban Transportation Patterns
Commuting in large cities limits the time and energy residents have for meal preparation. Reliance on convenience stores, street vendors, and grab-and-go meals—many of which are meat-based—reduces the feasibility of maintaining vegetarian diets consistently.
Marketing of Protein Supplements
Protein powders, bars, and shakes are often marketed as essential for strength and performance, with an emphasis on animal-derived proteins. Urban consumers, especially athletes and fitness enthusiasts, may perceive plant-based proteins as inferior, impacting vegetarian adoption rates.
Workplace Culture and Meal Options
Corporate and office cultures in urban areas often provide catered meals that prioritize meat dishes. Employees, even if interested in vegetarianism, may find few appealing alternatives, leading to gradual reintroduction of meat into their diets.
Urban Health Trends and Misconceptions
Urban populations are influenced by health trends and popular diets, some of which misrepresent vegetarian nutrition. Misinformation, such as claims that plant-based diets lack sufficient protein, discourages adoption despite scientific evidence supporting vegetarian health benefits.
Food Delivery App Influence
Apps like Uber Eats, DoorDash, and Grubhub often highlight meat-based restaurants more prominently than vegetarian options. Easy access to these foods and marketing prioritization shapes urban dietary choices, contributing to the decline in vegetarian meals.
Availability of Ready-to-Eat Vegetarian Products
Despite growing demand, ready-to-eat vegetarian meals are limited compared to meat-based options in urban grocery stores. The convenience gap makes maintaining a vegetarian diet more challenging for city residents with busy schedules.
Influence of Workplace Cafeterias
Urban workplaces often rely on cafeterias or on-site dining services. Vegetarian meals are frequently minimal, repetitive, or unappealing, causing employees to revert to omnivorous options, further contributing to declining plant-based eating habits.
Urban Family Meal Dynamics
Families in cities often share meals that prioritize convenience and popularity. Meat-based dishes dominate, especially in multi-generational households, making it difficult for individual members to maintain vegetarian diets consistently.
Influence of Urban Supermarkets
Urban supermarkets still allocate more shelf space to meat and dairy products than plant-based alternatives. This subtle environmental cue reinforces meat consumption and subtly discourages vegetarian shopping behaviors, particularly among casual buyers.
Impact of Holiday Traditions
Urban residents often follow traditional holiday meals that are heavily meat-centric, such as Thanksgiving turkey or Christmas ham. These seasonal indulgences can temporarily or permanently reduce adherence to vegetarian lifestyles, especially when they occur frequently.
Media Representation of Vegetarianism
Television, films, and online content frequently showcase non-vegetarian lifestyles as the norm. Urban populations consuming these media narratives are more likely to view vegetarianism as niche or inconvenient, contributing to its decline across major cities.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What are the most important Shocking Data Points about U.S. cities and vegetarianism?
The Shocking Data Points reveal declining vegetarian adherence, increased meat consumption, and uneven availability of plant-based foods across major U.S. cities.
2. How do Shocking Data Points explain dietary trends?
Shocking Data Points provide quantitative evidence showing how economic, cultural, and social factors influence residents’ choices to abandon vegetarian diets.
3. Why are these Shocking Data Points surprising?
They are surprising because despite growing awareness of health and environmental benefits, vegetarianism is declining in many urban areas, contrary to popular belief.
4. How can Shocking Data Points help public health planning?
Policymakers can use Shocking Data Points to identify neighborhoods with limited access to plant-based foods and implement targeted nutritional interventions.
5. What do Shocking Data Points say about meat consumption?
Shocking Data Points show that overall meat consumption has increased in most U.S. cities, even as interest in vegetarianism grows in niche communities.
6. How do Shocking Data Points relate to urban lifestyle?
They highlight how busy schedules, fast food availability, and workplace dining options contribute to declining vegetarian adherence in urban populations.
7. Can Shocking Data Points predict future dietary shifts?
Yes, by analyzing historical trends, Shocking Data Points help forecast potential growth or decline in vegetarian adoption over the coming years.
8. How do Shocking Data Points vary by region?
Shocking Data Points indicate significant regional differences; cities like Portland and Austin have higher vegetarian adoption, while others like Dallas and Miami show declines.
9. What role do Shocking Data Points play in nutrition research?
Researchers use Shocking Data Points to understand correlations between diet patterns, health outcomes, and socio-economic factors in urban populations.
10. Are Shocking Data Points consistent across all age groups?
No, Shocking Data Points show that younger urban residents are more likely to try vegetarian diets, while older generations are slower to adopt them.
11. How do Shocking Data Points reveal economic influences?
They show that higher-income areas tend to have better access to plant-based foods, while lower-income neighborhoods face cost barriers that discourage vegetarianism.
12. What do Shocking Data Points say about plant-based food availability?
Shocking Data Points reveal that specialty vegetarian products are less accessible in smaller cities or food deserts, impacting dietary choices.
13. How do Shocking Data Points affect environmental awareness?
They highlight that even in environmentally-conscious cities, residents may continue meat-heavy diets, suggesting awareness alone does not guarantee plant-based adoption.
14. Do Shocking Data Points reflect social influences?
Yes, they demonstrate that peer pressure, cultural norms, and family habits strongly affect urban residents’ willingness to maintain vegetarian diets.

15. How can Shocking Data Points improve education?
Shocking Data Points can guide schools and community programs to focus on nutrition education, cooking skills, and awareness campaigns about plant-based diets.
16. Are Shocking Data Points linked to health outcomes?
Yes, they indicate that cities with declining vegetarianism often report higher rates of obesity, hypertension, and related health issues.
17. What insights do Shocking Data Points provide for urban planning?
Urban planners can use Shocking Data Points to improve access to fresh produce, encourage farmers markets, and support local plant-based initiatives.
18. How do Shocking Data Points relate to marketing?
They reveal that aggressive marketing of meat products and protein supplements often overshadows vegetarian alternatives, influencing consumer behavior.
19. Can Shocking Data Points guide consumer choices?
Yes, they help residents understand local trends, availability, and barriers to vegetarianism, enabling more informed dietary decisions.
20. Why are Shocking Data Points important for future research?
Shocking Data Points provide a quantitative baseline for studying urban dietary trends, predicting shifts, and evaluating interventions aimed at promoting plant-based diets.





