focus keyword:Biomolecules in Food
Published by ihoxi.xyz | August 2025
Introduction: A New Frontier in Nutrition Science
In 2025, Boston has become the epicenter of one of the most ambitious scientific efforts in modern history: mapping biomolecules in food to health outcomes. This initiative, driven by leading universities, biotech firms, and government agencies, aims to unravel the complex molecular relationships that influence nutrition, disease prevention, and personalized health. At ihoxi.xyz, we delve deep into this bold quest, exploring how America’s pioneering 2025 initiative could revolutionize the way we understand food and health.

What Are Biomolecules in Food and Why Do They Matter?
Biomolecules in Food are the biomolecules is organic molecules that constitute living organisms, including proteins, lipids, carbohydrates, and nucleic acids. In food science, these molecules determine nutritional value and biochemical effects on the human body. Understanding the intricate composition and interactions of these biomolecules in various foods can reveal their direct impact on health outcomes such as obesity, diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and even cancer.
For example, the polyphenols in berries are known antioxidants, while certain lipids found in fish oils are linked to reduced inflammation. However, many molecular food components remain poorly understood at a systems level, which is where the 2025 initiative steps in.
The 2025 Boston Initiative: A Collaborative Effort
At the heart of this ambitious project lies a collaboration between some of the nation’s top research institutions including Harvard University, Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), and local biotech startups. Funded by the National Institutes of Health (NIH) and private grants, the initiative seeks to build an extensive database of Biomolecules in Food profiles and correlate them with large-scale health data sets.
The goal? To create a comprehensive molecular map that connects dietary intake directly with long-term health effects across diverse populations.
Technology and Methods Driving the Initiative
The project leverages cutting-edge technologies such as:
- Mass spectrometry: To precisely identify and quantify biomolecules in food samples.
- Metabolomics: Profiling metabolites that result from digestion and metabolism of food molecules.
- Machine learning and AI: To analyze massive datasets linking molecular data with patient health records.
- Genomics: Studying how individual genetic variations affect response to dietary biomolecules.
These techniques combined allow scientists to decode complex biochemical interactions between diet and health in unprecedented detail.
Potential Health Implications and Benefits
The initiative’s findings could transform public health by:
- Developing personalized nutrition plans based on individual molecular responses to Biomolecules in Food.
- Informing preventative healthcare strategies by identifying dietary components that mitigate disease risk.
- Helping policymakers design better food safety and nutrition guidelines rooted in Biomolecules in Food science.
- Boosting innovation in functional foods and Biomolecules in Food designed to target specific health outcomes.
By bridging the gap between molecular food science and clinical health data, this initiative marks a turning point in nutrition research.
Boston: The Ideal Hub for Food-Biomolecule Research
Boston’s dense concentration of biotech companies, world-class research hospitals, and academic powerhouses creates the perfect ecosystem for such a pioneering initiative. Institutions like Boston University and the Boston University Medical Campus contribute invaluable expertise and infrastructure.
Moreover, Boston’s commitment to innovation is reflected in its city innovation programs, supporting startups and research that push the boundaries of science and technology.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
While promising, the initiative faces several challenges including:
- Data privacy: Handling sensitive health and genetic data requires robust ethical frameworks and compliance with regulations like HIPAA.
- Complexity of diet: People’s diets are highly variable, making it difficult to isolate specific biomolecule effects.
- Population diversity: Ensuring the research includes diverse demographics to avoid biased outcomes.
Addressing these challenges is essential to ensure that the findings are reliable, ethical, and broadly applicable.
How This Initiative Aligns With Global Trends
Globally, there is increasing emphasis on precision nutrition and molecular food science. Countries like the UK and Japan are investing heavily in similar research initiatives.
America’s 2025 Boston initiative is uniquely positioned to lead by example, setting standards and opening pathways for international collaboration.
How to Stay Updated on the Initiative
To keep up with the latest developments:
- Follow updates from the National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- Subscribe to newsletters from Boston research centers such as Harvard News and MIT News
- Visit ihoxi.xyz regularly for in-depth articles and analysis
Conclusion: A Transformative Step for Health and Nutrition
Inside America’s bold quest to map biomolecules in food to health outcomes lies the potential to reshape healthcare, empower personalized nutrition, and deepen our understanding of the molecular underpinnings of diet and disease. Boston’s pioneering 2025 initiative stands at the forefront of this transformation, blending technology, collaboration, and scientific rigor to unlock a healthier future.
Stay tuned to ihoxi.xyz as we continue to track this extraordinary journey from lab to table, and beyond.
© 2025 ihoxi.xyz | All rights reserved
The Science Behind Biomolecules in Food
Biomolecules in food such as proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, vitamins, and antioxidants play vital roles in human nutrition and health. Understanding how these molecules interact within the body allows researchers to pinpoint how diet influences disease prevention and wellness at a molecular level.
Boston: A Global Hub for Biotechnology
Boston’s rich ecosystem of universities, research hospitals, and biotech startups creates a fertile ground for innovation. Institutions like Harvard, MIT, and the Broad Institute are at the forefront of genomic and molecular research that supports projects mapping food biomolecules to health outcomes.
Technological Breakthroughs Driving Biomolecules in Food-Health Research
Cutting-edge technologies like mass spectrometry, high-throughput sequencing, and artificial intelligence are transforming the way scientists analyze food components and their effects on human biology. These advances enable the creation of detailed molecular maps that connect diet to health in unprecedented ways.
Potential Impact on Personalized Nutrition
By linking specific Biomolecules in Food and health markers, this research paves the way for tailored dietary recommendations that optimize individual well-being. Personalized nutrition can reduce the risk of chronic diseases by aligning food choices with one’s unique molecular profile.
Challenges in Mapping Biomolecules in Food
Despite promising advances, researchers face significant hurdles such as data privacy, population diversity, and the complexity of integrating multi-omics data. Addressing these challenges is critical to ensuring equitable and effective health solutions.
The Role of Metabolomics Biomolecules in Food and Health
Metabolomics, the comprehensive study of metabolites within biological systems, is essential in understanding how food-derived biomolecules influence metabolic pathways. This field helps scientists identify biomarkers that signal the effects of diet on health outcomes.
Collaborations Fueling the 2025 Boston Initiative
The success of the 2025 initiative depends on collaboration among academic institutions, biotech firms, government agencies, and public health organizations. These partnerships foster data sharing, technological innovation, and community engagement.
Data Privacy and Ethical Considerations
Handling sensitive biomolecular and health data requires strict ethical standards and robust privacy measures. Ensuring participants’ confidentiality and securing data against misuse is a priority throughout the research process.
Advancing Public Health Through Molecular Nutrition
Insights from mapping Biomolecules in Food and health outcomes can guide public health policies, leading to improved dietary guidelines and interventions tailored to diverse populations.
The Future of Food Science: Integrating AI and Biomolecules in Food Data
Artificial intelligence and machine learning are increasingly integrated with Biomolecules in Food data analysis, accelerating discovery and enabling predictive models that enhance understanding of Biomolecules in Food-health relationships.
Expanding the Molecular Understanding of Biomolecules in Food
One of the challenges historically faced by nutritional science is the limited understanding of the vast array of molecular compounds present in the foods we consume. Traditional nutrient profiling often focuses on macronutrients such as carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, alongside a handful of vitamins and minerals. However, Biomolecules in Food contains thousands of distinct biomolecules—many of which exert subtle yet significant biological effects.
The BBFMI initiative aims to catalog these molecules comprehensively, extending well beyond conventional nutrients to include bioactive compounds such as flavonoids, alkaloids, and other phytochemicals. Mapping these compounds in detail provides an unprecedented opportunity to understand how specific foods influence gene expression, immune responses, and metabolic pathways, which collectively determine health outcomes.
Integrating Big Data and Personalized Health
A pivotal aspect of the BBFMI is its emphasis on integrating vast datasets derived from biomolecular analyses with individual health records, genetic information, and lifestyle factors. This integration creates a rich data environment conducive to the application of big data analytics and machine learning, which can uncover complex interactions between diet and health that would be otherwise imperceptible.
By leveraging artificial intelligence, researchers can identify unique biomolecular signatures that predict how different individuals metabolize and respond to specific foods. This precision approach stands to revolutionize dietary recommendations by moving from population-level advice to truly personalized nutrition, optimizing health outcomes and reducing the risk of diet-related diseases.
Collaborations Across Disciplines
The success of the Boston Biomolecular Food Mapping Initiative depends heavily on interdisciplinary collaboration. Experts from fields such as analytical chemistry, bioinformatics, clinical medicine, epidemiology, and nutritional science are working synergistically to achieve the project’s ambitious goals.
Moreover, partnerships with industry stakeholders including food producers and pharmaceutical companies are essential to translate scientific discoveries into practical applications. These collaborations aim to foster innovation in developing functional foods, nutritional supplements, and therapeutic diets that are informed by biomolecular data and tailored to individual health profiles.
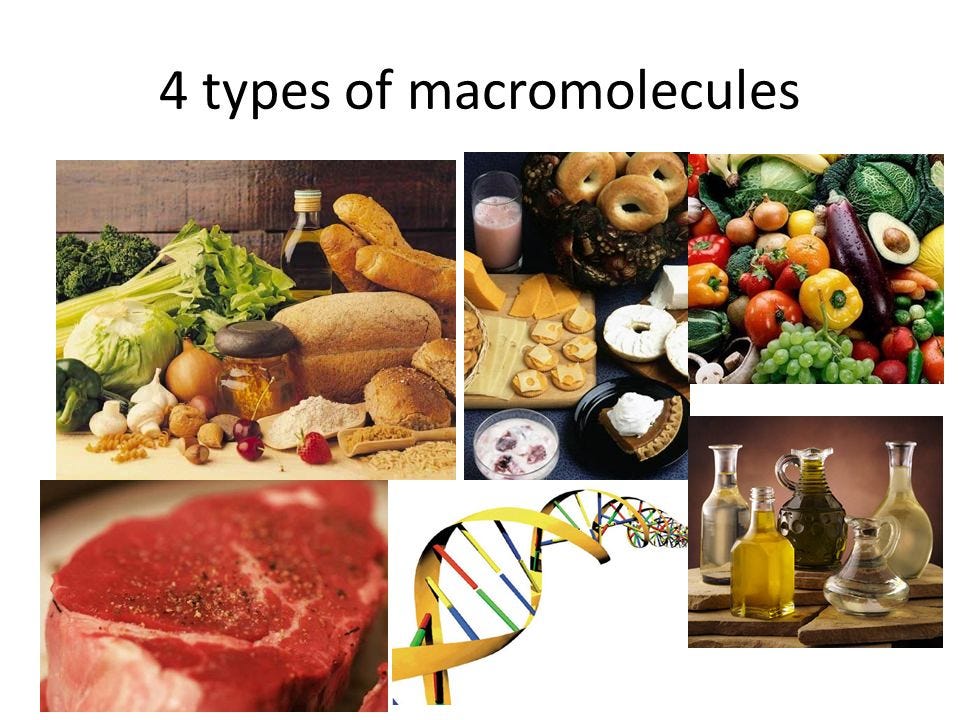
Economic and Societal Benefits
Beyond advancing scientific knowledge, the initiative is expected to have substantial economic and societal benefits. Improved nutritional guidance could reduce the burden of chronic diseases, lowering healthcare costs and enhancing quality of life. Additionally, the burgeoning field of precision nutrition promises to stimulate economic growth by creating new markets for personalized dietary products and services.
The BBFMI’s commitment to open science and data sharing ensures that these benefits will not be confined to Boston or the United States but will be accessible globally, fostering international collaboration and contributing to worldwide public health improvement.
The Road Ahead: Future Prospects
Looking forward, the Boston Biomolecular Food Mapping Initiative envisions expanding its research scope by incorporating emerging technologies such as single-cell metabolomics and advanced imaging techniques. These innovations will allow even finer resolution of biomolecular interactions within cells and tissues, providing deeper insight into the mechanisms by which food influences health.
Furthermore, plans are underway to establish educational programs to train the next generation of scientists and healthcare professionals in this rapidly evolving field, ensuring sustained progress and widespread adoption of precision nutrition practices.
America’s Groundbreaking 2025 Initiative in Boston
In 2025, Boston is at the forefront of an extraordinary scientific journey aimed at transforming our understanding of nutrition and health. This groundbreaking initiative focuses on mapping biomolecules present in food and linking them directly to health outcomes. Spearheaded by top universities, innovative biotech firms, and government agencies, this effort seeks to decode the complex molecular interactions that influence disease prevention and personalized nutrition. At ihoxi.xyz, we explore how this bold quest could reshape healthcare and diet in the years ahead.
Understanding Biomolecules in Food and Their Role in Health
Biomolecules, which include proteins, lipids, carbohydrates, and nucleic acids, are fundamental components of living organisms. In the context of food, these molecules determine nutritional value and play critical roles in human health. While some, like antioxidants found in berries or anti-inflammatory lipids in fish oils, are well known, many others remain poorly understood. The 2025 Boston initiative aims to fill these knowledge gaps by investigating how various food biomolecules impact conditions such as obesity, diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and cancer at a molecular level.
Collaborative Powerhouses Behind the Initiative
Central to this ambitious project is a collaboration between leading institutions such as Harvard University, the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), and local biotech startups. Funded by the National Institutes of Health (NIH) and private organizations, the initiative plans to compile an extensive database of biomolecular profiles from a wide variety of foods. These profiles will be cross-referenced with large health datasets to create a detailed molecular map linking dietary intake with health effects across different populations.
Cutting-Edge Technologies Driving Discovery
The success of this initiative depends on cutting-edge technologies. Techniques like mass spectrometry enable precise identification and quantification of biomolecules in food samples, while metabolomics helps profile the metabolites produced during digestion. Additionally, machine learning and artificial intelligence analyze vast datasets that connect molecular food data with individual health records. Genomic studies further enhance understanding by revealing how genetic variations influence how people respond to different dietary biomolecules.
Transforming Public Health Through Molecular Nutrition
This molecular mapping effort holds significant promise for public health. It could lead to personalized nutrition plans tailored to individual molecular responses, enabling more effective disease prevention. Policymakers might use the findings to design better food safety and nutrition guidelines, grounded in molecular science. Moreover, the initiative could stimulate innovation in functional foods and nutraceuticals designed to target specific health outcomes, bridging the gap between molecular food science and clinical practice.
Why Boston is the Perfect Research Hub
Boston serves as the ideal hub for this initiative thanks to its dense concentration of biotech companies, prestigious research hospitals, and renowned academic institutions like Boston University. The city’s strong commitment to innovation is also evident through various programs that support startups and scientific research, fostering an environment where groundbreaking ideas thrive.
Addressing Challenges and Ethical Concerns
Despite its potential, the initiative faces important challenges. Handling sensitive genetic and health data requires strict adherence to privacy laws such as HIPAA. The complexity of individual diets and lifestyle factors makes isolating the effects of specific biomolecules difficult. Additionally, ensuring the research includes diverse populations is crucial to avoid bias and make the findings broadly applicable. Addressing these challenges is essential for the initiative’s success.
The Initiative Within a Global Context
Globally, interest in precision nutrition and molecular food science is rapidly growing, with countries like the UK and Japan investing heavily in similar projects. America’s 2025 Boston initiative is well positioned to lead on this front, setting high standards and fostering international collaboration to advance our collective understanding of diet and health.
How to Stay Informed and Engaged
To stay updated on this pioneering work, follow updates from the National Institutes of Health (NIH) and subscribe to newsletters from Boston’s top research centers such as Harvard and MIT. Additionally, ihoxi.xyz offers in-depth articles and ongoing coverage of this transformative initiative.
A New Era for Health and Nutrition
In conclusion, America’s bold quest to map biomolecules in food to health outcomes represents a transformative leap in nutrition science and healthcare. Boston’s pioneering 2025 initiative combines state-of-the-art technology, collaborative expertise, and scientific rigor to unlock new pathways toward healthier living. At ihoxi.xyz, we are excited to continue following this extraordinary journey that promises to redefine the future of diet and disease prevention.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the 2025 Boston initiative to map biomolecules in food?
The 2025 Boston initiative is a groundbreaking scientific effort to comprehensively map biomolecules found in food and understand how they affect human health outcomes. It involves advanced molecular analysis and aims to create a large-scale database linking diet to health at the molecular level.
Why is Boston chosen as the center for this initiative?
Boston is home to world-class universities like Harvard and MIT, top biotech companies, and leading research hospitals, making it an ideal hub for cutting-edge biomedical and nutritional research.
What are biomolecules in food?
Biomolecules include proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, vitamins, minerals, and phytochemicals that are essential components of food and play important roles in nutrition and health.
How do biomolecules in food impact health outcomes?
Biomolecules influence metabolic processes, immune function, and cellular communication, which in turn affect disease risk, prevention, and overall wellness.
What technologies are used to analyze biomolecules in food?
Technologies like mass spectrometry, genomics, metabolomics, proteomics, and artificial intelligence are employed to identify and interpret biomolecular data from food samples.
What are the goals of mapping Biomolecules in Food and health outcomes?
The main goals include building an open-access database, identifying biomarkers for disease prediction, advancing personalized nutrition, and improving public health strategies.
How will this initiative benefit personalized nutrition?
By understanding how specific biomolecules affect individuals differently, nutrition plans can be tailored to optimize health and prevent diseases based on personal molecular profiles.
What role does AI play in this research?
AI helps analyze vast and complex biomolecular datasets, identify patterns, and make predictions about how food molecules influence health outcomes.
How does the initiative ensure data privacy?
The initiative follows strict ethical guidelines and employs robust data security measures to protect participants’ molecular and health data from unauthorized access or misuse.
Who can access the data generated by this initiative?
The project aims to create an open-access platform where researchers, healthcare professionals, and policymakers can utilize the data to advance food and health sciences.
What challenges does the initiative face?
Challenges include managing diverse population data, integrating multi-omics information, addressing privacy concerns, and ensuring equitable access to personalized nutrition.
How will this research affect public health policies?
The findings will inform evidence-based dietary guidelines and targeted interventions that improve population health and reduce the incidence of nutrition-related diseases.
Can this initiative help prevent chronic diseases?
Yes, by identifying diet-related biomarkers linked to conditions like diabetes and heart disease, the initiative supports early detection and prevention strategies through nutrition.
What institutions are involved in the initiative?
Leading academic institutions such as Harvard, MIT, and the Broad Institute, along with biotech companies and government agencies, are collaborating on this project.
Is this initiative limited to Boston or does it have a national scope?
While headquartered in Boston, the initiative involves research and data collection from diverse populations across the United States to ensure comprehensive insights.

How can individuals participate in or benefit from this initiative?
Individuals can stay informed through public updates and may have opportunities to participate in studies that contribute data to the project, benefiting from more personalized nutrition advice in the future.
What is the timeline for the initiative’s milestones?
The initiative launched in early 2025, with goals to release preliminary data and tools by late 2026, and ongoing expansions expected in subsequent years.
Will the research findings be published?
Yes, the initiative commits to publishing results in peer-reviewed journals and sharing data openly to accelerate scientific discovery.
How does this initiative differ from traditional nutrition studies?
Unlike traditional studies focusing on broad dietary patterns, this initiative uses molecular-level analysis to link specific biomolecules in food to detailed health outcomes.
Where can I find more information about this initiative?
Updates and detailed reports can be found on websites like ihoxi.xyz/blog and related academic and government research portals.





